Abstract
Background: Patients with B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) relapsed after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation have poor prognosis. Donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) have shown limited success in the setting of relapse by a mere increase in median survival by 6 months and a significant risk of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and additional risk of marrow aplasia. The second generation chimeric antigen receptor-T cell (CAR-T) for CD19 is a promising treatment for relapsed and refractory B-ALL, but the effectiveness and safety of donor-derived second generation of CD19 CAR-T cell infusion for relapsed B-ALL after allogenic stem cell transplantation have not been determined.
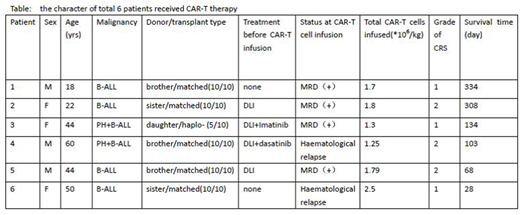
Methods: Between July 2017 and June 2018, 6 adult patients with B-ALL relapsed (2 patients were hematologic relapsed; 4 patients were minimal residual disease(MRD)-positive) after allogenic stem cell transplantation were enrolled, including 5 sibling-matched stem cell transplantation and 1 haploidentical transplantation . Donor's T cells were infected with lentivirus carrying CD19 CAR plasmid which containing CD19 scfv (HI-19 clone) and 4-1BB-CD3ζ signaling domains to generate CAR-T cells. Patients received FAC (fludarabine:25-30mg/m2/d*3, cyclophosphamide:350mg/m2/d*2, cytosine arabinoside:100mg/m2/d*4) pretreatment and then total (1.25-3.5)*106/kg donor-derived 4-1BB CAR-T cell were infused in consecutive 2 or 3 days .
Results: All the patients achieved MRD negative remission and complete donor chimerism. Three patients experienced grade 2 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and received 6-8mg/kg interleukin-6 receptor blocker (tocilizumab) treatment ; the other 3 just experienced grade 1 CRS. None of these patients needed glucocorticoid treatment. No patients developed acute or chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Now all the 6 patients are alive and show complete donor chimerism with MRD negative remission. The median follow-up time are 243.5days.
Conclusion: Donor-derived second generation of CD19 CAR-T cell treatment for relapsed B-ALL after allogenic stem cell transplantation were effective and safe, which may be confirmed with more clinical studies.
Key words: donor-derived CD19 CAR-T cell therapy, allogenic stem cell transplantation, B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, relapse
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.